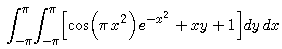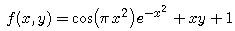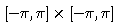Double Integrals I
Part 2: Double Integrals Over Coordinate Rectangles
Next we study the integral
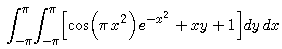
that is, the integral of
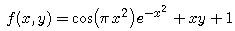
over the rectangle
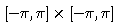
- Define the function f(x,y) in your worksheet, and graph it over the given rectangle. If necessary, rotate the graph until you are sure you have a good mental image of the function.
- Your worksheet includes commands to calculate an approximation to the value of the double integral. Explain briefly what is being calculated and why it approximates the integral.
- Calculate the estimates for n = 10, 20, 40, and 80. How many terms are in the last sum?
- On the basis of these calculations, give your estimate of the value of the integral. Be careful to include only as many digits in your approximation as you believe to be accurate.
- Design a more efficient numerical approximation, and use it to estimate the integral for n = 10 and 20. Calculate and record the approximations.
- Now we want to get as good an estimate as possible for the double integral. Do as much hand calculation as you can. You should be able to reduce the computation to evaluation of a single one-variable definite integral. Use your helper application to approximate this integral. Compare the result with the estimate from your numerical method. The two estimates should be close. If they are not, do whatever you need to do to resolve the difference.